Birth trauma refers to injuries that happen to a baby during delivery. While the term birth injury is usually used to describe something that affects a baby’s body system, the phrase birth trauma encompasses injury to the baby’s tissues and organs, as well as the long-term consequences of the injury, such as cerebral palsy, hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE), Erb’s palsy, seizures and intellectual disabilities.
Traumatic birth injuries are often caused by mechanical force, but can also be caused by the overuse of delivery drugs, abnormal presentation, the negligent use of forceps or vacuum extractors, attempts at delivering babies that are too big to fit through the mother’s pelvis, and attempts at delivering a baby whose shoulders are stuck. Doctors can often avoid birth trauma by following best care practices and being skilled in handling labor and delivery complications.
my canadian pharmacy @ online pharmacy @ online masters in pharmacy @ mexico pharmacy @ pharmacy in la canada
 The terms ‘birth trauma’ and ‘birth injury’ are often interchangeable, but birth trauma is usually thought of as being caused by mechanical damage, while the term birth injury typically refers to injury caused by a lack of oxygen to the baby’s brain or a brain infection, such as meningitis.
The terms ‘birth trauma’ and ‘birth injury’ are often interchangeable, but birth trauma is usually thought of as being caused by mechanical damage, while the term birth injury typically refers to injury caused by a lack of oxygen to the baby’s brain or a brain infection, such as meningitis.
Labor and delivery can be traumatic for the baby. However, if the medical team avoids risky practices, such as misuse of the labour drugs Pitocin and Cytotec and negligent use of forceps or vacuum extractors, and the physician quickly delivers the baby as soon as distress is evident on the fetal heart monitor, most instances of birth trauma can be avoided.
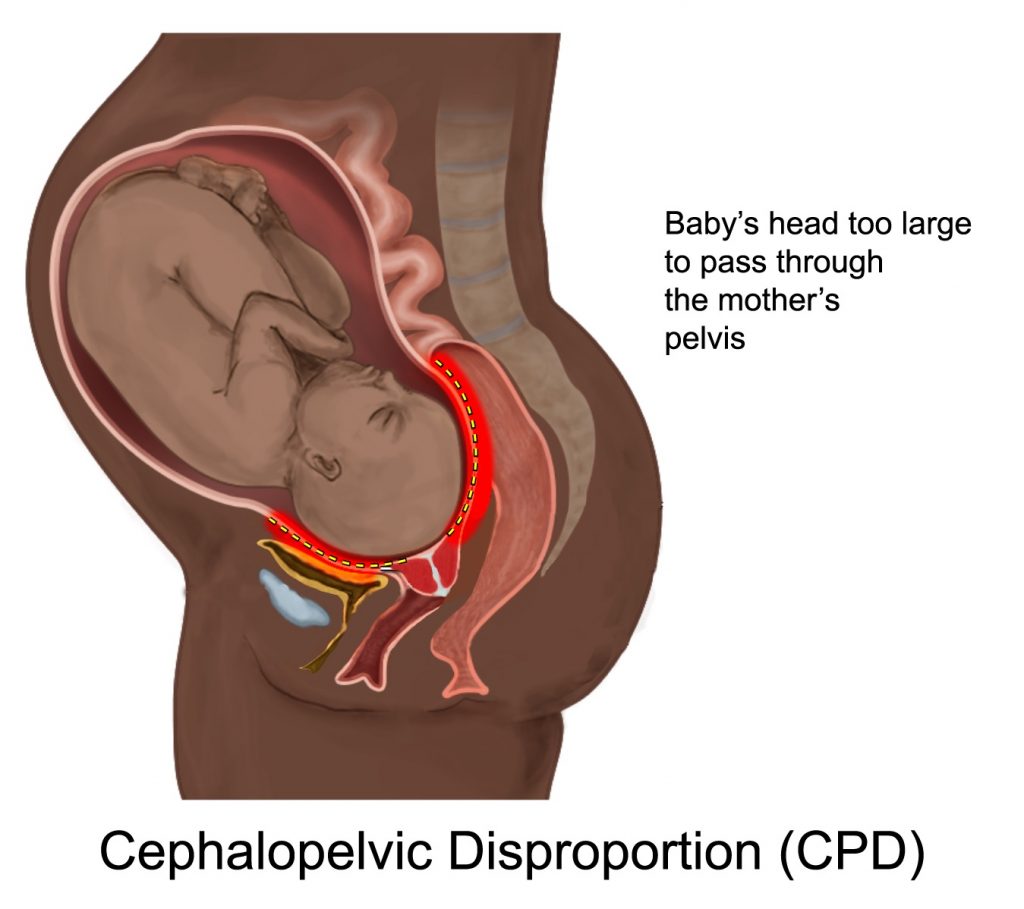
It also is important for the physician to be aware of any size or positional problems with the baby. Attempts at vaginal delivery when the baby is too big for the size of the mother’s pelvis (cephalopelvic disproportion / CPD) or when the baby’s shoulder is stuck on the mother’s pelvis (shoulder dystocia) can cause the baby to experience permanent nerve damage, trauma to the skull, brain bleeds and hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE). Most of these conditions can cause cerebral palsy and seizures.

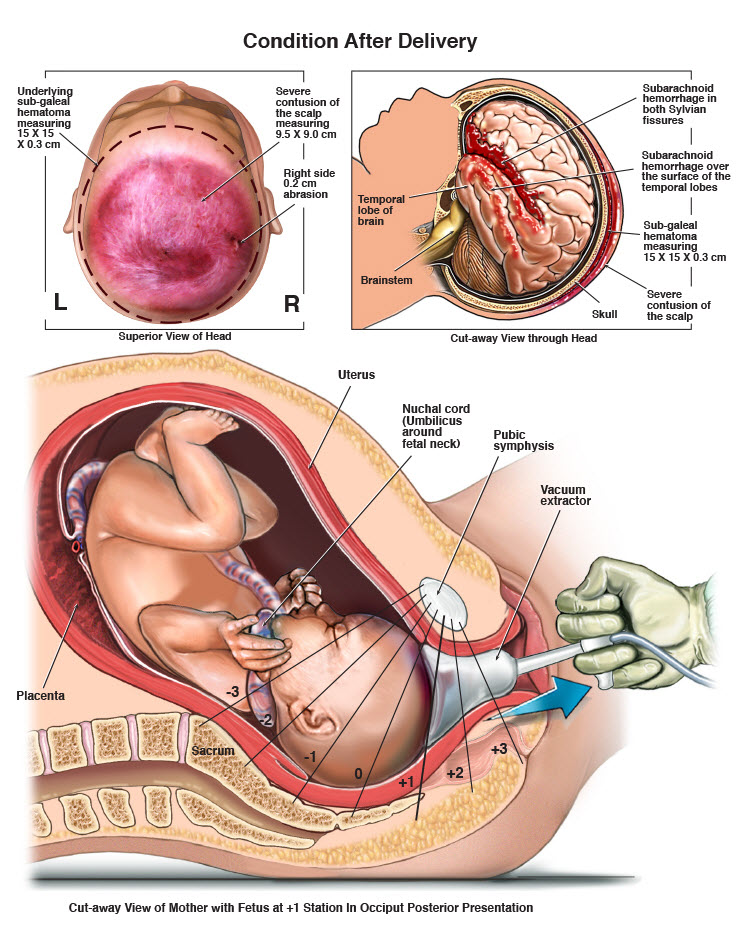
 In some cases, physicians may use forceps or vacuum extractors to assist with vaginal delivery. During attempts at delivery, if the physician applies too much pressure to her head in order to deliver her, this can cause the nerves in the shoulder area, called brachial plexus nerves, to stretch and tear, which can cause partial or full paralysis of the arm. This arm paralysis is called Erb’s palsy. Use of forceps and vacuum extractors can not only cause Erb’s palsy, but can also cause brain bleeds and hemorrhages and resultant cerebral palsy.
In some cases, physicians may use forceps or vacuum extractors to assist with vaginal delivery. During attempts at delivery, if the physician applies too much pressure to her head in order to deliver her, this can cause the nerves in the shoulder area, called brachial plexus nerves, to stretch and tear, which can cause partial or full paralysis of the arm. This arm paralysis is called Erb’s palsy. Use of forceps and vacuum extractors can not only cause Erb’s palsy, but can also cause brain bleeds and hemorrhages and resultant cerebral palsy. Extracranial hemorrhages. These are brain bleeds that occur just outside the skull, and they can be life threatening.
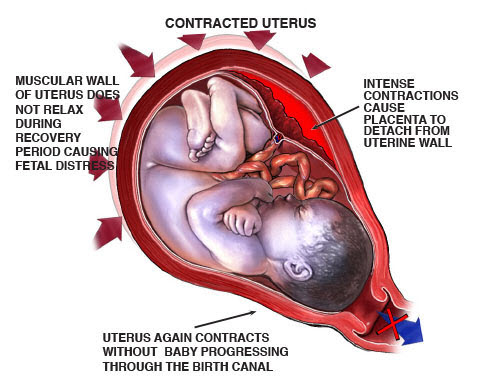
Extracranial hemorrhages. These are brain bleeds that occur just outside the skull, and they can be life threatening. In many instances, a C-section is required. Repeated attempts at vaginal delivery – especially in instances in which vaginal delivery is against the standard of care – can cause brain bleeds and other traumatic injuries that can cause hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy and cerebral palsy. When any signs of distress appear on the fetal heart rate monitor, the baby must be delivered as quickly as possible, and C-section delivery is usually the best and safest way to do this.
In many instances, a C-section is required. Repeated attempts at vaginal delivery – especially in instances in which vaginal delivery is against the standard of care – can cause brain bleeds and other traumatic injuries that can cause hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy and cerebral palsy. When any signs of distress appear on the fetal heart rate monitor, the baby must be delivered as quickly as possible, and C-section delivery is usually the best and safest way to do this.

